Benefits and Drawbacks of the Pneumatic Waste System
Pneumatic waste systems have long been thought to be exclusive to the design and industrial sectors. Memos were sent through a complicated network, much like the Jetsons-style tube systems of a early 1900s. Since the 1960s, major cities around the world have relied on pneumatic tube waste disposal systems. These include the likes of London, Stockholm, & Barcelona. Pneumatic underground disposal is being considered as an increasingly viable option to meet the growing demand for hygienic waste disposal.
How It All Works
This is how the pneumatic waste disposal system works. There are indoor and outdoor units for residents to separate their waste, each of which accepts a specific type of waste. The waste is sent down to a valve room via a septic system. Waste flows through a pneumatic robot arm that can be electronically activated or deactivated by control room operators. The waste is compressed in a compactor before being taken from off island via a vacuum-sucked 20-inch tube system travelling at 30-60 mph. It’s considered a simple & elegant system, but it’s been around since the 1970s and requires a lot of maintenance.
Is There Hope for the Future?
There are numerous advantages to using a pneumatic waste system, but there are also numerous drawbacks. These drawbacks may be due more to the system’s outdated design than anything else. To put it another way, engineers are constantly called upon to repair tears as well as remove blockages in the chute, which can either result in the entire disposal system being down for a period of time or the engineers having to avoid traffic.
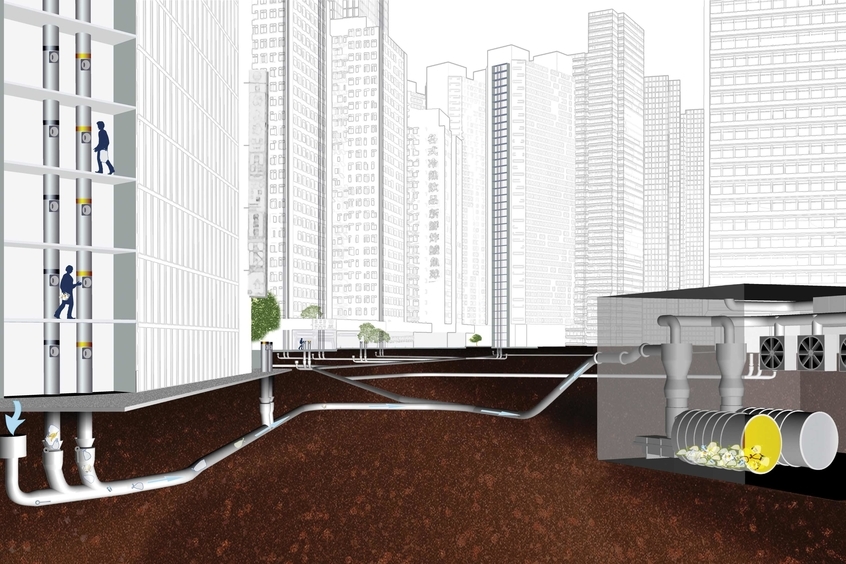
The pneumatic waste system’s main advantages are in terms of money and the environment. The operation requires fewer employees than the more traditional method of waste collection involving trucks. As a result, wage costs are reduced. As a result, vehicle costs such as fueling and purchasing this same vehicles themselves are completely eliminated.
In addition, it provides a sanitary means of getting rid of waste. As a result, vehicle emissions are no longer a priority. Residents will benefit from a cleaner environment, garage trucks will no longer obstruct general traffic, streets will look better without bins trying to line the pavements, and truck-related accidents will no longer be a problem. Overall, pneumatic waste disposal systems are considered to be safer, more cost-effective, and better for the environment than traditional methods.
Improving on the negative aspects. It is not cost effective to use pneumatic waste disposal systems in low density areas, and even when they are, not everything can be gathered by the tubes. For example, a suction tube can’t accept bulk wastes such as appliances, furniture, and other items that are fed into a garbage truck’s back.
In spite of these drawbacks, the design discussion can be enriched by bringing service infrastructure into play and raising important questions regarding public space. There are many factors to consider when developing or implementing a pneumatic waste disposal system, such as the costs and benefits of the current strategy.



